3D Printing
The most popular 3D file formats for product develoment
Aug 3, 2020
Have you ever worked on a 3D model only to realise no one else on the team had the right software to open it? 3D modelling is an essential part of any hardware project. However, there are many different 3D file formats and each one is used in a different context and includes different features.
In this guide, we'll go through some of the most popular 3D file formats, discovering when to use them and how they can help you with product development.
Definition and types
A 3D file is a digital object that stores information about one or more three-dimensional objects. There are many different 3D file formats, and they usually allow the user to view, edit and even manufacture the 3D model.
The information contained in a 3D file depends on the format. The different types of information that a file can include are the following:
Geometry: The file includes 3D models that are usually defined with points, lines or equations. Depending on the format, the surface of the model can be a mesh, which has a limited quality, or parametric surfaces, which allow for more detailed surfaces.
Scene: This refers to the position of the 3D model regarding to the different planes. It also considers lights and camera for those files used for model rendering.
Appearance: Textures and colours applied to the model's surface. Only some formats include this type of information. Depending on the manufacturing technology used, this information may be ignored. For example, FDM 3D printing (Fused Deposition Modelling) cannot usually print objects with multiple colours.
There is no perfect 3D file format. Each one is unique, and you need to choose one that adapts to your industry's needs.
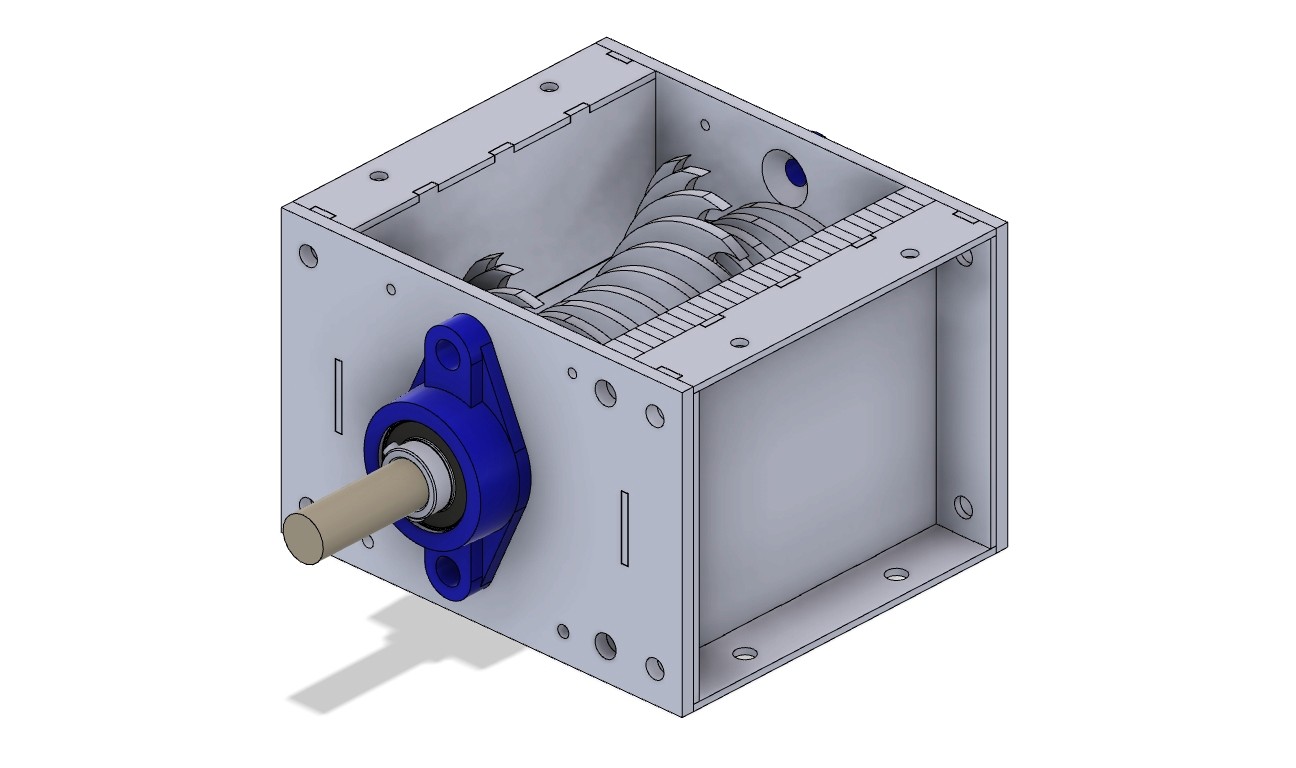
3D model of a Precious Plastic Shredder open in Autodesk Fusion 360
3D file formats can also be divided into two categories based on who created them and the context in which they are used.
3D file formats based on who created them:
Proprietary: These formats are developed by software companies as the main format for their specific 3D modelling tool. They work well, but they are usually not compatible with any other software. For example, a design in F3D format (Autodesk Fusion 360) cannot be opened in SolidWorks.
Neutral: There are neutral and open formats developed by independent organisations. They're quite popular as they're compatible with most 3D modelling software.
3D file formats based on when they are used:
Design: These file formats are used during the design process as it's easy to edit the 3D model, appearance and scene. For example, if you're designing in Rhino, you will probably save the files using their own 3D file format (3DM).
Manufacturing: It's common to export designs from a proprietary format to a neutral format for manufacturing as it's critical that the manufacturing partner can properly open the file and transform the design into a product. Once you finish your Rhino design in 3DM format, you also export it in STL format for manufacturing.
3D file formats for design
.SLDPRT: This is the standard file format used in SolidWorks. It's a proprietary format and it can be combined with the SLDASM format, which combined multiple SLDPRT files creating an assembly. It is usually used for complex CAD designs and it's popular in the engineering and manufacturing industries.
.STEP: The STEP or STP format is one of the most popular neutral file formats. It covers all the information needed to make a product, including shapes, features, material properties and more. It is supported by most 3D modelling software and it's editable, being recommended for collaborative projects. Also, this format is also suitable for manufacturing.
.F3D: The F3D format is the default file format in Autodesk Fusion 360. Even though the files are usually stored in their cloud service, it's possible to export them. It includes different types of information, including 3D models, scenes and attributes. It's a fairly new format and it's being quickly adopted by designers and engineers.
.BLEND: Blender's own file format is one of the most complete ones. It allows storing data about 3D models, colours, textures, scenes and even animations. This software is used in the design, video game and animation industries.
.3DS: This format is used in Autodesk 3ds Max. It's similar to Blender's file format, as it stores all the information, including designs and animations. It's used in the video game and animation industries, and it's a very popular format as the 3D modelling software was released in 1996.
.SKP: It's used in SketchUp, an accessible 3D modelling software used mainly for concept designs and renders. It's a popular format among interior designers and architects.
.IGS: This neutral file format is still one of the most popular ones despite the fact that the STEP format was supposed to replace it. It is compatible with many 3D modelling tools.
.3DM: Used as the standard format in Rhino and Grasshopper. It is popular in the industrial design and architecture industries due to the complex models it can generate, which can be stored in the 3DM files as parametric surfaces or simpler meshes.
.IPT: The Autodesk Inventor format is similar to the Solidworks or Autodesk Fusion 360 files as it can store high-quality 3D models. Due to Autodesk's software portfolio, Inventor is also capable of working with 2D files. Multiple IPT files can be combined into a .IAM assembly file.
3D file formats for manufacturing
.STL: It's the most popular format in the digital fabrication industry. The 3D models are represented as a triangular mesh with variable density, no colours, textures or scenes are included. It is used during testing, especially with 3D printing, as the mesh can be easily processed to manufacture functional prototypes. It is not the most suitable format for complex manufacturing methods such as CNC machining.
.OBJ: Very popular alternative to STL files. It is supported by most 3D modelling tools. Apart from 3D models, if combined with an MTL format file, you can include textures and colours. This makes it one of the best formats to prototype using color 3D printers such as the HP Jet Fusion series.
.3MF: Also known as 3D Manufacturing Format, it's a neutral format supported by Microsoft, Autodesk, Ultimaker and more. This format was created as an advanced substitute to the old STL format. It packages 3D models and additional information such as manufacturing setting for 3D printing or the model's appearance.
.DAE: This file format is called COLLADA (COLLAborative Design Activity). It was originally planned as a format to move data from one software to another, and it's compatible with most 3D modelling tools, game engines and other software tools. It's recommended when one product is designed with many different tools.
.PLY: Inspired by OBJ, PLY file format was developed mainly to store information captured by 3D scanners. The files include meshes as well as colours, textures. It is supported as an export format for some 3D modelling tools.
.STEP: This design file format can also be used during the manufacturing process and it's compatible with almost any type of design.
2D file formats for manufacturing
There are dozens manufacturing methods currently available, and even though the most complex ones are based on 3D models, there are other ones, such as laser cutting, who work with 2D vector files.
Many 3D modelling tools allow you to import and export 2D files. For example, Autodesk Fusion 360 can import 2D files in formats such as DXF or SVG that allow you to extrude those 2D shares and transform them into 3D models. On other 3D modelling tools you can choose a face or cut of a 3D model and export it as a 2D file.
Some of the most common 2D file formats used for product development include DWG, DXF, DWF, SVG and even PDF.

Fusion 360 2D file import feature that allows extrusion of vector files
Document your project with the 3D viewer
Sharing 3D files with your team members is the best way to see how development is going and to gather feedback. However, in many cases, it isn't even necessary to send the source file and ask them to open it.
With Wikifactory's 3D viewer you can easily show your team member the design progress. You just need to embed the 3D model from your project on your project's description or on a Wikifactory page. No plugins required. Here is an example with the Otto DIY robot 3D model.
Conclusion
Design with the software you feel comfortable with and make sure that it's suitable for the type of product you are designing. Also, make sure you can export the 3D models in different formats that are compatible with manufacturing tools and the software your team members use.
We hope this article provides a useful guide for you to understand better the different 3D file formats that are available. If you found this article helpful, help others by liking and sharing it.
Get the latest articles on your inbox

